Tablets prescribed for anxiety or depression typically belong to classes of medications known as antidepressants or anxiolytics. It’s important to note that the choice of medication depends on the specific symptoms, the diagnosis, and individual factors. Medications for anxiety and depression should be prescribed and monitored by a healthcare professional. Here are common classes of medications used for anxiety and depression:
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs):
- Examples: Sertraline (Zoloft), Fluoxetine (Prozac), Escitalopram (Lexapro).
- Mechanism: Increase serotonin levels in the brain.
- Usage: First-line treatment for both anxiety and depression. Generally well-tolerated with fewer side effects.
- Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs):
- Examples: Venlafaxine (Effexor), Duloxetine (Cymbalta).
- Mechanism: Increase levels of serotonin and norepinephrine.
- Usage: Effective for depression and certain anxiety disorders.
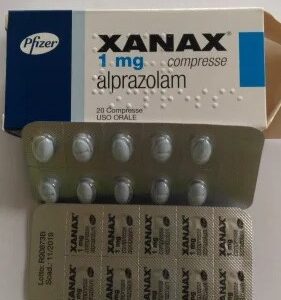
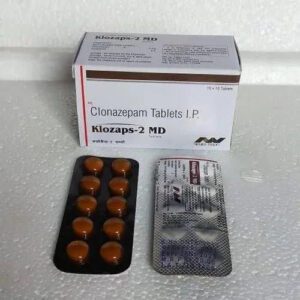
- Benzodiazepines (Anxiolytics):
- Examples: Alprazolam (Xanax), Clonazepam (Klonopin), Diazepam (Valium).
- Mechanism: Enhance the effects of GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) in the brain.
- Usage: Short-term relief for acute anxiety. Not typically used as a first-line treatment for depression due to the risk of dependence.
- Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs):
- Examples: Amitriptyline, Nortriptyline.
- Mechanism: Increase levels of norepinephrine and serotonin.
- Usage: Second-line treatment for depression or anxiety when SSRIs or SNRIs are not effective.
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs):
- Examples: Phenelzine (Nardil), Tranylcypromine (Parnate).
- Mechanism: Inhibit the activity of monoamine oxidase, leading to increased levels of neurotransmitters.
- Usage: Reserved for cases where other medications have not been effective. Requires dietary restrictions.
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate medication based on an individual’s specific symptoms, overall health, and potential side effects. Psychotherapy (counseling or therapy) and lifestyle modifications are often recommended in conjunction with medication for a comprehensive treatment plan. Always follow the prescribed dosage and guidelines provided by the healthcare provider.
Showing 1–9 of 11 results